When we talk about "technology in translation," we're talking about the powerful software and digital tools that help human translators do their job. It’s not about replacing people with machines. Instead, it’s a partnership designed to make the whole process faster, more consistent, and capable of handling the massive amount of content the world produces today.
This blend of skilled linguists and smart systems moves translation far beyond simple word-for-word swapping, tackling the complex demands of global communication head-on.
How Technology Is Reshaping Translation

Picture a master craftsman from a century ago, carefully carving a beautiful sculpture from a block of wood. Every detail is perfect, but it takes an incredible amount of time. For a long time, that’s what translation was like—a purely manual, artful process. It was precise, but slow and nearly impossible to scale up.
Now, think of that same craftsman in a modern workshop, surrounded by sophisticated power tools. They still have all their skill and expertise, but the new tools help them work faster and more efficiently. They aren't just carving one sculpture; they're producing a dozen in the same amount of time, all with the same quality. That’s the reality of technology in translation today.
The Shift from Manual to Augmented Workflows
The world moves fast. Businesses need to launch products in ten countries at once, and customers expect support in their native language. Media companies have to dub and subtitle shows for global audiences in days, not months. The old, manual way of translating just can't keep up with this demand.
This is where the right tools make all the difference. Technology handles the heavy lifting and repetitive tasks, which lets human linguists focus on the irreplaceable, high-value work they excel at:
- Cultural Nuance: Making sure a clever slogan in English doesn't become offensive or nonsensical in Japanese.
- Creative Content: Adapting persuasive ad copy or literary prose so it has the same emotional impact in a new language.
- Strategic Oversight: Guiding complex projects, maintaining a consistent brand voice, and making the final call on quality.
- Complex Terminology: Ensuring that precise legal, medical, or engineering terms are translated perfectly.
The point isn't to take humans out of the loop. It's to elevate their role. Technology becomes a powerful sidekick, allowing one linguist to accomplish what it might have taken a whole team to do just a decade ago.
What Modern Translation Technology Includes
The modern translation "workshop" is filled with specialized tools. It’s not just a dictionary and a word processor anymore. We’re talking about an integrated system where machine translation engines provide a solid first draft, translation memories instantly recall previously approved phrases to ensure consistency, and management platforms organize the entire workflow from start to finish.
This is the synergy that makes modern global communication possible. It’s the perfect combination of human expertise and machine efficiency, and we'll be diving into each of these core components throughout this guide.
The Role of AI and Machine Translation
At the very core of today's translation technology is Machine Translation (MT). You can think of it as the powerful engine that does the initial, heavy lifting—taking text in one language and converting it into another. But not all MT is created equal. The technology has come a very long way.
To really see how far we've come, let's take a quick look back at how this technology has changed over the years.
Evolution of Machine Translation Technology
| Technology Type | How It Works (Analogy) | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-Based MT (RBMT) | A student with a dictionary and a grammar book. | Predictable, good for simple structures. | Clunky, literal, and easily confused by idioms or context. |
| Statistical MT (SMT) | A student who has read millions of translated documents and finds the most probable word sequences. | Better fluency than RBMT. | Can sound unnatural and sometimes produces grammatically incorrect "word salad." |
| Neural MT (NMT) | A student who has lived abroad and understands the feel of the language, not just the words. | Fluent, context-aware, and handles complex grammar well. | Can still make subtle errors; requires massive datasets to train. |
As you can see, the journey from rigid, rule-based systems to the more intuitive neural networks has been a huge leap for the industry.
The Rise of Neural Machine Translation
The real turning point was the arrival of Neural Machine Translation (NMT). Instead of following a strict set of man-made rules, NMT models learn by sifting through massive volumes of human-translated texts. This process teaches them to recognize patterns, context, and the subtle ways words relate to each other.
This is why NMT can generate translations that are so remarkably fluent and human-like. It’s the difference between a word-for-word substitution and a translation that captures the original meaning and tone.
NMT models can:
- Grasp context from entire sentences or paragraphs, not just single words.
- Navigate complex grammar and sentence structures far more effectively.
- Produce natural-sounding text that needs much less editing.
The jump in quality is what has made MT a genuinely useful tool in professional workflows. To see what makes this possible under the hood, these machine learning code examples offer a more technical look.
The Human-in-the-Loop Model
Even with NMT’s power, the goal isn't to take humans out of the picture entirely. This is where the Post-Editing Machine Translation (PEMT) workflow comes in. PEMT is a hybrid model: an AI generates the first draft, and then a professional human translator steps in to review, refine, and perfect it.
This approach gives you the best of both worlds—the sheer speed of a machine combined with the nuance and expertise of a human. The AI does the grunt work, while the linguist adds the final polish, checking for accuracy, cultural relevance, and brand voice.
This diagram shows the trade-offs between a purely human process and a machine-first approach.
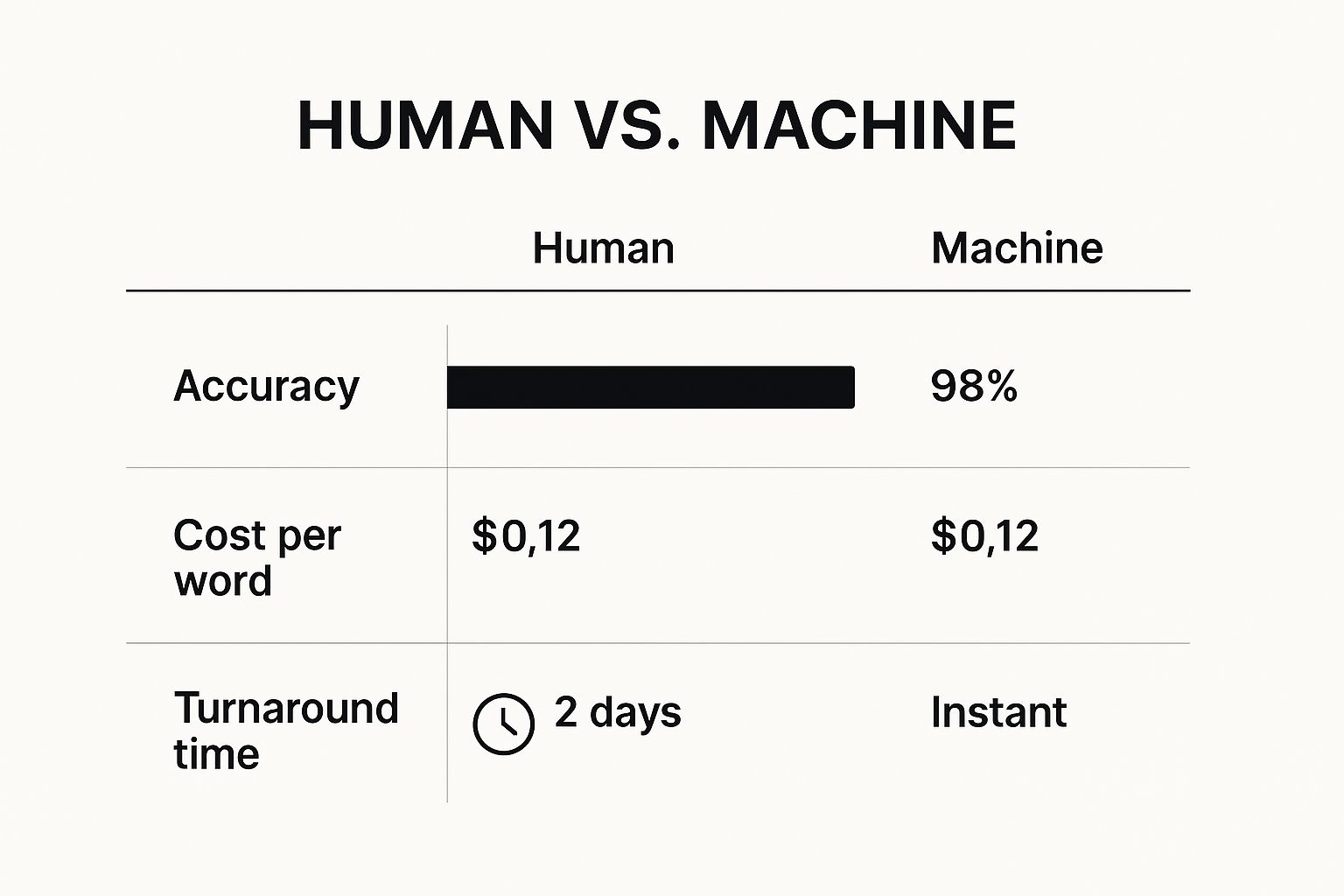
While human translation still sets the gold standard for accuracy, the PEMT model offers a powerful balance of quality, speed, and cost.
The Growing Market and What Drives It
This constant improvement in MT has lit a fire under the industry. The global machine translation market was valued at USD 668.3 million in 2025 and is on track to hit around USD 1,012.2 million by 2032.
This growth is all thanks to the technology's ability to produce more contextual, human-sounding translations. This is powered by something called Natural Language Processing (NLP), which is essentially how computers learn to understand and use human language.
If you're curious about how that works, you can find a deeper dive into the world of NLP here: https://ziloservices.com/blogs/the-power-of-natural-language-processing-nlp-applications-use-cases-and-impact-in-2025/
Ultimately, AI and machine translation have created a new standard. They've shifted the translator’s role from a creator of first drafts to a high-level editor and quality controller, making global communication faster and more scalable than ever before.
Inside the Professional Translator's Toolbox
While raw machine translation provides a powerful engine, professional linguists are working from a sophisticated cockpit of integrated tools. These platforms aren't designed to automate translators out of a job. Far from it. They're intelligent workbenches built to amplify human expertise, drive efficiency, and lock in unwavering consistency across every single project.
Think of a skilled surgeon. They don't just walk into an operating room with their bare hands; they have a tray of precision instruments, each designed for a specific task. The same is true for today's translators, and the most fundamental of these instruments are Computer-Assisted Translation (CAT) tools.
The Intelligent Workbench of CAT Tools
It's a common misconception that CAT tools are just a fancy name for machine translation. In reality, they serve a very different purpose. A CAT tool is a software environment that places the original and translated text side-by-side, but its real magic lies in the features that support and augment the human translator.
At the heart of any CAT tool is its Translation Memory (TM). Imagine you’re translating a 200-page user manual for a new smartphone, and the phrase "Swipe up to unlock" appears 37 times. Without a TM, you'd have to translate that phrase 37 separate times, opening the door to tiny, frustrating inconsistencies.
A Translation Memory is essentially a smart database of your own past work. It automatically saves every sentence you translate and approve. The next time an identical or similar sentence pops up, the TM instantly suggests the approved translation, saving you time and guaranteeing consistency.
This feature is an absolute game-changer for technical, legal, or marketing content where specific phrases and brand terminology have to be perfect every time. For a global brand, making sure a slogan is translated the same way across thousands of documents isn't just nice—it's essential for brand identity.
Building on Past Success with Translation Memory
Translation Memory is smart enough to work on more than just exact matches. It also flags "fuzzy matches"—sentences that are similar but not identical. For example, if you've already translated "Click the blue button to save," the TM might recognize "Click the red button to save" as an 85% fuzzy match.
The CAT tool highlights what's different, letting the translator make a quick edit instead of retyping the whole thing from scratch. This system pays off in several huge ways:
- Drastic Time Savings: Translators can stop wasting time re-translating content they've already perfected.
- Improved Consistency: Every document, from a website FAQ to a technical datasheet, uses the exact same terminology.
- Reduced Costs: Clients often pay less for repeated segments, since a good chunk of the work is already done.
By building on past work, a CAT tool and its Translation Memory create a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement, making each project faster and better than the last.
Orchestrating Global Content with a TMS
If a CAT tool is the translator's individual workbench, then a Translation Management System (TMS) is the control center for the entire factory floor. For big organizations juggling projects across multiple languages, teams, and time zones, a TMS is the air traffic controller that keeps everything from crashing.
A TMS is a centralized platform that puts the entire localization workflow on rails. It becomes the single source of truth for project managers, translators, editors, and clients. Instead of drowning in endless email chains, spreadsheets, and file transfers, everyone operates within one unified ecosystem.
Take a software company getting ready to launch a new app in 15 languages. Using a TMS like Phrase or Smartling, they can manage the whole process. The system can automatically assign tasks to available linguists, track progress in real-time, and ensure everyone is using the most up-to-date files and glossaries.
Key functions of a modern TMS usually include:
- Workflow Automation: Automatically pushing content from translation to editing to final review.
- Centralized Resources: Housing all Translation Memories, termbases, and style guides in one accessible place.
- Project Tracking: Providing clear dashboards that show the status of every language and task at a glance.
- Seamless Integration: Connecting directly with content management systems (CMS), code repositories, and other business tools.
This integration is what enables a truly hands-off content pipeline. A marketing team can publish a new blog post, and the TMS can automatically pull the text, send it for translation, and push the translated versions right back to the website without anyone lifting a finger. This is how technology helps businesses operate at a genuinely global scale.
Automating Workflows and Enhancing Quality
So far, we've looked at the tools a translator uses day-to-day. But behind the scenes, another layer of technology is at work, orchestrating entire projects and ensuring quality from the very start. These systems are the backbone of any serious global content strategy, making sure everything is delivered fast and meets the right standards. This is where we move from fixing mistakes after the fact to preventing them in the first place.
A huge part of this shift is Quality Estimation (QE). The easiest way to think of QE is as an AI proofreader that checks the machine's work before a human ever sees it. The moment a sentence comes out of the machine translation engine, the QE tool scans it and gives it a quality score.
This one step changes everything. Instead of a human editor slogging through every single translated line, the system can intelligently flag only the sentences that are likely to have problems. A segment with a high score might be approved with just a quick glance, while a low-scoring one gets sent for a full human post-edit.
The Role of Quality Estimation Tools
This smart routing is all about focusing human expertise where it actually makes a difference. QE tools help teams stop treating all content as equal and start prioritizing their effort. It’s a much more efficient way to work.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Targeted Human Review: Linguists can breeze past the high-quality machine output and dive deep into the tricky segments that need a human touch.
- Faster Turnaround Times: Projects get done much quicker because you’re dramatically cutting down the volume of content that needs a full manual review.
- Predictable Quality: Companies get a clear picture of their MT output quality before the human editing process even begins, which helps with planning and budgeting.
This kind of smart automation is a core principle of any efficient modern business. To see how these ideas apply on a larger scale, you can read more in our guide to business process automation.
Advanced Terminology Management
While Translation Memory keeps full sentences consistent, termbases (sophisticated terminology management tools) handle the critical individual words and phrases. A termbase isn't just a simple glossary; it’s a living, central database that defines how key terms must—and must not—be translated.
For a medical device company, this means ensuring "catheter" is translated perfectly across dozens of languages and hundreds of documents. For a software brand, it’s what keeps a feature name like "Insight Dashboard" from being translated when it shouldn't be.
A modern termbase is a brand’s linguistic rulebook. It enforces brand voice, technical accuracy, and legal compliance by providing translators with approved terminology in real-time, right within their CAT tool.
Creating a Continuous Content Loop
The final piece of the automation puzzle is connecting all these translation systems directly to a company's Content Management System (CMS). This creates a seamless, hands-off loop for global content.
Imagine a marketing team publishes a new blog post. An API connection can instantly detect that new content, pull it into the Translation Management System, and kick off the entire translation workflow. Once finished, the translated versions are pushed right back to the website, ready to go live—often without anyone lifting a finger. This is how modern technology manages the global content pipeline, from creation straight through to publication.
This kind of integration is essential in a market where speed and scale are everything. The broader language services industry, which covers translation, localization, and interpretation, was valued at around USD 60.68 billion in 2022 and is expected to hit nearly USD 96.21 billion by 2032. Europe is the biggest player, making up 49% of the market. To get a sense of how tech helps streamline content right from the source, check out these methods for recording and transcribing a Zoom conference with specialized tools.
Breaking Down Barriers With Real-Time Translation

So far, we've focused on tools that have mastered the written word. But what about live, spoken conversation? This is where the real action is happening now, with technology in translation aiming to erase language delays in everything from high-stakes business meetings to global conferences and even just navigating a foreign country.
Picture this: you're in a tense negotiation with a potential business partner. Instead of waiting for an interpreter, you speak into a device, and your words come out in their native language almost instantly. They reply, and you hear their response in English just as quickly. This isn't a scene from a sci-fi movie anymore; it's a reality being fine-tuned by some of the most advanced AI available today.
How Instant Speech Translation Works
At its heart, real-time translation is a lightning-fast, three-step relay race run by a team of AI models. It all has to work in perfect harmony.
- Speech-to-Text (STT): First, an AI model listens to what's being said and converts the spoken words into written text.
- Machine Translation (MT): That text is immediately passed to a neural machine translation engine—the same kind we've already discussed—which translates it into the target language.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): Finally, another AI takes the translated text and turns it back into natural-sounding speech.
This entire sequence unfolds in a matter of seconds, giving the impression of a smooth, uninterrupted conversation. When evaluating these systems, it's crucial to look at platforms that offer robust multilingual support to see just how many language pairs they can handle well.
The Next Step: Voice Preservation and Cloning
One of the biggest knocks against real-time translation has always been the output. It often sounds robotic, stripping a conversation of its personality and emotional nuance. But a fascinating new technology called voice cloning or voice preservation is changing the game entirely.
This tech analyzes the unique fingerprint of a person's voice—their specific pitch, tone, and rhythm—and applies those same qualities to the translated audio. The result? The translation sounds like the original person is speaking it, just in a different language.
This isn't just a cool party trick. By preserving a speaker's vocal identity, you create a far more authentic and trustworthy experience. A virtual business meeting feels more personal, and a presenter can connect with a global audience on a much deeper level.
This kind of innovation is what’s fueling the real-time speech translation market. Projections show it’s on track to hit around USD 1.8 billion by 2025, largely because users are demanding more natural interactions. Voice preservation is a huge piece of that puzzle, with the voice cloning market itself expected to reach USD 1 billion by 2025.
What we're seeing is a clear path toward a future where language is no longer an obstacle to spontaneous, genuine human connection.
What’s the Future for Human Translators in an AI World?
The rise of AI has everyone in the translation industry asking the same question: are human translators on their way out? But the answer isn't a simple "yes" or "no." Instead of being a replacement, technology is becoming a powerful partner, pushing the translator's role away from pure wordsmithing and toward something far more strategic.
We're seeing the emergence of a new kind of professional: the localization consultant. This isn't someone who just translates text. They are tech-savvy managers who ensure cultural nuances land perfectly and handle the kind of creative, emotionally complex content that still trips up even the best AI. Their value isn't measured by words per hour anymore, but by their skill in orchestrating the entire localization process.
A New Era Demands New Skills
To thrive, translators have to adapt, adding more technical and strategic skills to their linguistic talent. The job is shifting from just producing words to providing high-level oversight and quality control.
Here are the skills that really matter now:
- Expert Post-Editing: It's one thing for a machine to translate text; it's another for it to sound natural. Experts need to be able to quickly scan AI-generated content and polish it, catching subtle mistakes in tone and context that machines miss.
- Technology Management: Being proficient with tools like CAT tools and TMS platforms is non-negotiable. It's about managing terminology and ensuring consistency across huge projects.
- Cultural Consulting: This is where human expertise really shines. A consultant can offer deep insights into local customs and slang, making sure a marketing campaign connects with its audience instead of falling flat.
By mastering these skills, translators become strategic partners, not just production vendors. They leverage the information from these tools to guide their clients, which requires a sharp, analytical mind. You can actually see how this works in practice by reading our article on data-driven decision making.
The future of translation isn’t about humans versus machines. It’s a partnership. Technology does the heavy lifting—the repetitive, high-volume work—which frees up human experts to provide the creativity, strategy, and cultural insight that technology can't replicate.
This human-in-the-loop approach is the smartest way forward. Machines give us speed and scale, but humans provide that crucial final layer of judgment and polish. This synergy ensures that global content is not only fast and affordable but also accurate, impactful, and genuinely human.
Frequently Asked Questions
As these new tools reshape the translation world, a lot of good questions come up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to clear up how this technology actually works in practice.
Will AI Make Human Translators Obsolete?
Not a chance. The goal here isn’t replacement; it's teamwork. AI, especially neural machine translation, is a beast when it comes to plowing through massive volumes of straightforward text. It can produce a decent first draft at a speed no human could ever match.
But where it falls short is in the subtleties—the cultural nuances, clever marketing slogans, or highly technical content that demands a true subject matter expert. This is where the human translator’s role is shifting. Professionals are becoming more like localization consultants and tech-savvy editors, adding that crucial final polish and strategic thinking that a machine simply can't replicate.
What Is the Difference Between a CAT Tool and MT?
This is a fundamental concept to get right. Think of Machine Translation (MT) as the engine itself—the part that does the raw, automatic translation.
A Computer-Assisted Translation (CAT) tool, however, is the entire workshop. It's the sophisticated software environment a professional translator uses to work smarter, not just harder. A CAT tool brings together everything they need: Translation Memory (TM) to recycle past translations, termbases for brand consistency, and yes, often an MT engine as just one of the tools in the toolkit.
To put it simply: MT does the translating. A CAT tool helps a human do the translating better, faster, and more consistently.
Can I Trust Machine Translation for Important Documents?
It depends entirely on what the document is for. Need to get the general idea of an internal email or a foreign news article? Modern Neural Machine Translation (NMT) is usually good enough. The quality has improved by leaps and bounds, making it a solid choice for low-risk content where you just need speed.
However, for anything your customers will see, anything legally binding, or anything that represents your brand, you absolutely need a human in the loop. The industry standard is Post-Editing Machine Translation (PEMT). This is where a professional linguist takes the AI’s output and meticulously refines it to ensure it’s accurate, culturally appropriate, and hits the right tone. For high-stakes content, never just "set it and forget it" with raw machine translation.
At Zilo AI, we provide the expert human oversight needed to perfect your global content. Our skilled linguists and data specialists ensure your message is not just translated, but truly localized. Learn more about our multilingual services at ziloservices.com.

