In today's interconnected business ecosystem, the line between internal teams and external providers is increasingly blurred. For organizations scaling teams and managing third-party data or manpower providers, success hinges on more than just finding the right vendors. It demands building a strategic, resilient, and high-performing network of partners. A generic, one-size-fits-all approach is a recipe for operational bottlenecks, data security vulnerabilities, and missed opportunities for innovation.
Effective vendor management strategies are no longer a back-office function; they are a critical competitive differentiator. The ability to systematically select, manage, and optimize vendor relationships directly impacts everything from product quality and speed to market to overall business agility and profitability. Poor vendor oversight can introduce unacceptable risks, while a well-executed strategy transforms your supplier base from a simple cost center into a powerful engine for growth.
This guide moves beyond surface-level advice to provide a comprehensive collection of nine actionable strategies tailored for modern business challenges. You will learn how to implement practical frameworks for:
- Strategic Vendor Segmentation to focus your resources effectively.
- Performance Scorecards and KPIs to measure what truly matters.
- Risk-Based Assessments to proactively mitigate potential threats.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis to understand the complete financial impact of a partnership.
From mastering the contract lifecycle to fostering robust vendor relationships, each strategy is designed to provide clear, implementation-focused insights. Let’s dive into the methods that will help you build a vendor ecosystem that actively drives your organization's success.
1. Strategic Vendor Segmentation
Not all vendors are created equal, and one of the most effective vendor management strategies is to stop treating them as if they are. Strategic Vendor Segmentation is a systematic approach to categorizing suppliers based on their business impact, spend volume, and relationship complexity. This allows you to allocate resources, manage risks, and nurture relationships more effectively, moving beyond a one-size-fits-all model.
By classifying vendors into tiers such as Strategic, Preferred, and Approved, organizations can tailor their engagement strategies. A high-spend, high-dependency technology partner like Microsoft, which is critical to core operations, requires a different management style than a low-risk, easily replaceable office supply provider.
How to Implement Vendor Segmentation
The core of this strategy lies in creating a clear classification framework. This process involves a cross-functional analysis of each vendor against predefined criteria.
-
Define Your Tiers: Establish distinct categories. A common model includes:
- Strategic Partners: Highly integrated, critical to your business success, and difficult to replace. These relationships focus on joint innovation and long-term value.
- Preferred Suppliers: Important for operations and offer significant value, but have viable alternatives. The goal here is performance optimization and cost-effectiveness.
- Approved Vendors: Transactional relationships for non-critical goods or services where cost and efficiency are the primary drivers.
-
Set Clear Criteria: Use a scorecard approach combining factors like annual spend, risk level (operational, financial, data security), and strategic importance. For example, a data annotation provider handling sensitive customer information would rank high on the risk scale, regardless of spend.
The following hierarchy diagram visualizes a common three-tier segmentation model, showing how spend and complexity typically correlate across different vendor categories.
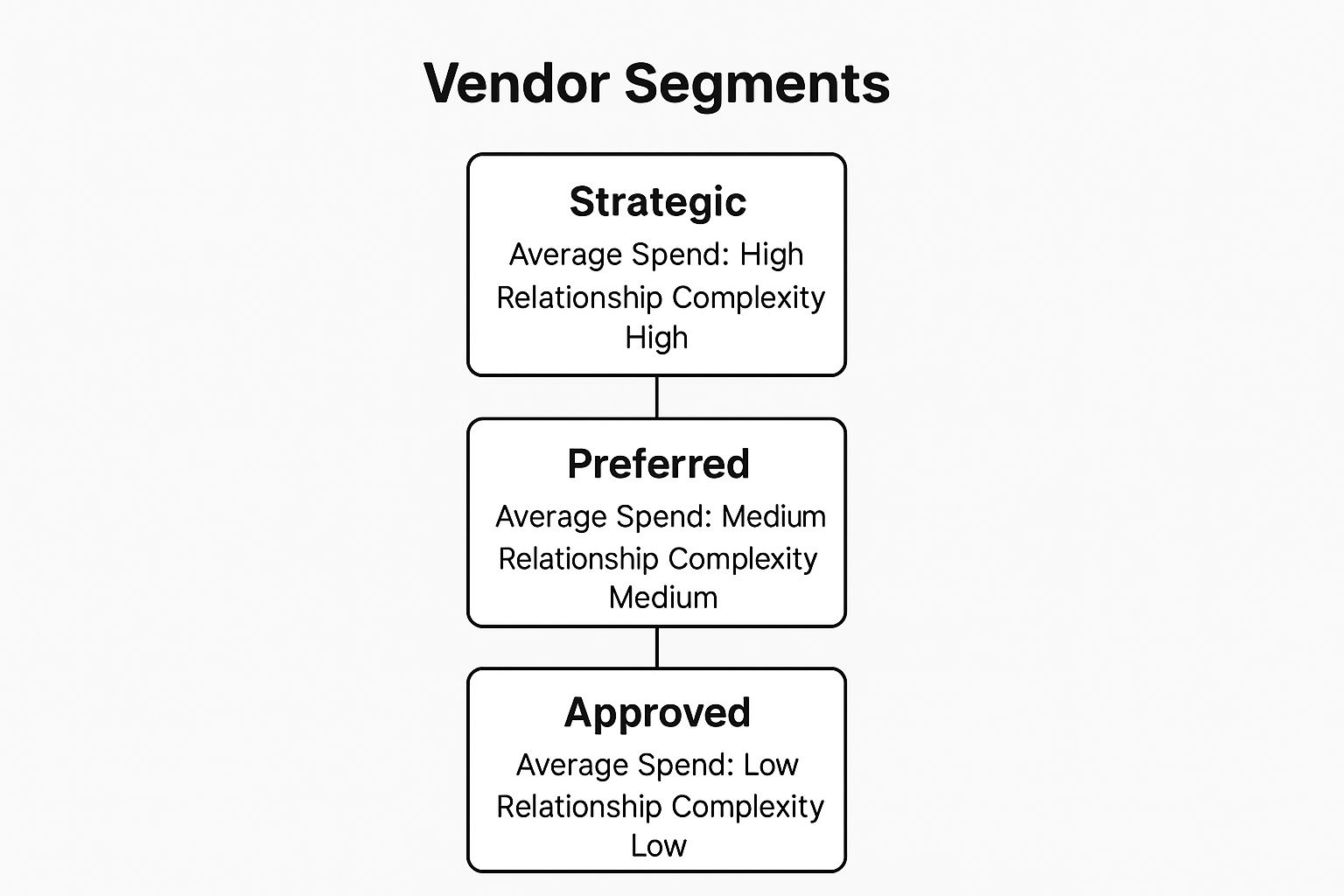
As the infographic illustrates, as you move up the hierarchy from Approved to Strategic vendors, the relationship becomes more complex and the financial investment grows, demanding more intensive management.
2. Vendor Performance Scorecards and KPIs
Effective vendor management strategies rely on data, not just intuition. Implementing Vendor Performance Scorecards is a systematic approach to measuring, tracking, and evaluating supplier performance against predefined metrics. This strategy moves beyond simple cost analysis, creating a holistic view of a vendor’s contribution to your organization across dimensions like quality, delivery, service, and innovation.
By using a combination of quantitative and qualitative Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), you can provide objective feedback, identify areas for improvement, and make informed, data-driven decisions. This structured approach transforms vendor relationships from subjective partnerships into transparent, performance-based collaborations. For instance, Amazon uses detailed vendor dashboards to monitor critical fulfillment metrics, ensuring its supply chain operates at peak efficiency.
As the infographic shows, a balanced scorecard includes a mix of metrics covering key performance areas, providing a comprehensive and objective view of vendor value.
How to Implement Vendor Scorecards
The key to a successful scorecard system is involving vendors in the process and ensuring the metrics are aligned with your business goals. This fosters buy-in and drives collaborative improvement.
-
Define Core Metrics: Establish clear, measurable KPIs across relevant categories. A common framework includes:
- Quality: Defect rates, accuracy percentages (e.g., for data annotation), and adherence to specifications.
- Delivery: On-time delivery rates, lead time accuracy, and order fulfillment speed.
- Cost: Price competitiveness, total cost of ownership, and adherence to budget.
- Service & Responsiveness: Communication effectiveness, issue resolution time, and overall support quality.
-
Establish a Scoring System: Assign weights to each KPI based on its importance to your business objectives. Use a simple, clear scoring scale (e.g., 1-5 or a percentage-based system) to rate performance. For companies focused on innovation, like Procter & Gamble, metrics related to new product ideas or process improvements might carry a heavier weight.
-
Schedule Regular Reviews: Performance data is only useful if it’s acted upon. Set up quarterly business reviews (QBRs) to discuss scorecard results with your vendors. Use these sessions to celebrate successes, address shortfalls, and collaboratively develop action plans for continuous improvement. By making this a core part of your process, you can strengthen your ability to make data-driven decisions. For more insights, explore how to build a culture of data-driven decision-making with Zilo Services.
3. Risk-Based Vendor Assessment
A proactive approach to vendor management is crucial for protecting your business, and a Risk-Based Vendor Assessment strategy moves you from a reactive to a preemptive stance. This methodology involves systematically identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks associated with each vendor relationship throughout its entire lifecycle. It protects your organization from a wide array of threats, including operational disruptions, financial instability, compliance failures, and reputational damage.
This strategy acknowledges that every vendor introduces a unique risk profile. A data annotation provider with access to sensitive customer information presents a different set of risks than a logistics partner. By assessing these risks upfront and continuously monitoring them, you can build a more resilient and secure supply chain. For example, JPMorgan Chase’s robust third-party risk management program includes continuous financial health monitoring to preemptively address supplier instability.

How to Implement Risk-Based Vendor Assessment
Implementing this strategy requires a structured, cross-functional process to create and maintain comprehensive risk profiles for all your suppliers.
-
Develop Risk Assessment Templates: Create standardized questionnaires and scorecards tailored to different vendor categories (e.g., technology, data services, fulfillment). For more detailed guidance on assessing potential suppliers, explore strategies for effectively evaluating fulfillment partners. These templates should cover key risk domains:
- Operational Risk: Assess the vendor's ability to deliver services without interruption (e.g., business continuity plans, dependency on subcontractors).
- Financial Risk: Evaluate the vendor's financial stability to ensure they remain a viable partner.
- Compliance & Legal Risk: Verify adherence to industry regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and other legal requirements.
- Cybersecurity Risk: Scrutinize data protection policies, security certifications, and incident response plans.
-
Establish Continuous Monitoring: Risk is not a one-time check at onboarding. Implement automated tools and regular manual reviews to monitor key risk indicators (KRIs) such as financial health alerts, negative press, or cybersecurity vulnerability reports. Involve legal, compliance, and IT security teams in these ongoing assessments to ensure comprehensive oversight.
4. Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM)
Vendor relationships are governed by contracts, yet many organizations manage these critical documents in a fragmented, manual way. Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM) is a systematic, end-to-end approach to managing vendor agreements, from initial request and authoring to negotiation, execution, performance monitoring, and eventual renewal or termination. This is one of the most crucial vendor management strategies for mitigating risk and maximizing value.
By centralizing contracts and automating workflows, CLM transforms static documents into strategic assets. It provides a single source of truth, ensuring that terms are enforced, obligations are met, and compliance is maintained. For instance, Siemens leveraged a digital CLM system to streamline its global operations, while Johnson & Johnson reduced its contract cycle times by an impressive 40% with a similar enterprise-wide initiative.
How to Implement Contract Lifecycle Management
Effective CLM implementation hinges on combining technology with standardized processes to create a seamless, transparent, and efficient system.
-
Standardize and Automate: Begin by creating a library of pre-approved contract templates. This minimizes legal review cycles and ensures consistency. Implement automated approval workflows to route contracts to the right stakeholders, eliminating bottlenecks and manual handoffs.
-
Integrate and Analyze: A powerful CLM system does not operate in a silo. Integrate it with your procurement, finance, and vendor management platforms to create a unified data ecosystem. To truly streamline and optimize your vendor agreements, a comprehensive approach to Master Contract Lifecycle Management is essential. Use the system's analytics to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify renewal opportunities, and flag potential compliance issues before they escalate.
-
Focus on Adoption: Technology is only effective if people use it. Provide thorough training for all users on the new CLM processes and tools. Regularly audit contract data quality and system performance to ensure the platform continues to meet business needs and drive a strong return on investment.
5. Vendor Relationship Management (VRM)
Effective vendor management strategies extend beyond contracts and performance metrics; they are built on strong, collaborative relationships. Vendor Relationship Management (VRM) is a strategic approach that shifts the focus from purely transactional interactions to building long-term, trust-based partnerships with key suppliers. This fosters mutual value, drives innovation, and creates a significant competitive advantage.
Instead of viewing vendors simply as service providers, VRM treats them as integral extensions of your team. This is particularly crucial for strategic or high-dependency partners whose capabilities are deeply intertwined with your business objectives. For example, Apple's deep collaboration with manufacturing partners like Foxconn is not just about production; it's a partnership that drives manufacturing innovation and operational excellence, directly impacting product launches.
How to Implement Vendor Relationship Management
Adopting a VRM mindset requires a deliberate investment in communication, governance, and shared goals. The focus is on creating an environment where both parties are motivated to succeed together.
-
Establish Clear Governance and Communication: Implement a regular cadence of meetings, from operational check-ins to executive business reviews. This ensures alignment, provides a forum for strategic discussions, and helps proactively address challenges before they escalate.
-
Create Shared Goals and Incentives: Move beyond one-sided SLAs. Develop joint scorecards with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that reflect mutual success. Consider incentive structures that reward vendors for innovation, cost savings, or exceptional performance that directly benefits your business.
-
Invest in Relational Skills: Equip your procurement and vendor management teams with more than just negotiation tactics. Train them in communication, conflict resolution, and collaborative problem-solving to build and maintain strong interpersonal connections with their vendor counterparts.
-
Involve Vendors in Strategic Planning: For your most critical partners, provide visibility into your long-term roadmap. Involving them in early-stage planning for new projects or products allows them to align their own development and resource allocation, leading to better support and more innovative solutions for your organization.
6. Vendor Diversity and Inclusion Programs
Beyond simple procurement, modern vendor management strategies increasingly focus on creating a positive societal impact and driving business innovation. A Vendor Diversity and Inclusion Program is a strategic initiative to actively increase spending with diverse suppliers, including businesses owned by minorities, women, veterans, LGBTQ individuals, and other underrepresented groups. This approach transforms the supply chain from a cost center into a powerful tool for corporate social responsibility and competitive advantage.
By intentionally engaging with a broader range of suppliers, companies like General Motors and IBM have discovered new sources of innovation, enhanced brand reputation, and strengthened community relationships. This strategy is not just about meeting quotas; it's about building a more resilient, agile, and representative supply chain that reflects the diverse markets a company serves.
How to Implement a Vendor Diversity Program
A successful program requires commitment, clear goals, and a structured implementation plan. It involves moving beyond passive acceptance to actively seeking out and developing diverse supplier relationships.
- Set Measurable Goals: Establish specific, quantifiable targets for diverse supplier spend. For example, aim to increase spending with women-owned businesses by 15% year-over-year. Tying these metrics to procurement team performance evaluations creates accountability.
- Provide Capacity Building: Many diverse suppliers are smaller businesses that may need support to meet the demands of a large enterprise. Offer mentorship, training, and resources to help them scale their operations, ensuring they can grow alongside your business.
- Partner with Certification Bodies: Leverage organizations like the National Minority Supplier Development Council (NMSDC) or the Women's Business Enterprise National Council (WBENC) to identify and vet certified diverse suppliers.
- Implement Tier-2 Programs: Encourage your prime (Tier-1) suppliers to develop their own diversity initiatives. Including tier-2 diverse spend requirements in your primary contracts amplifies your program's impact throughout the entire supply chain.
By integrating these steps, you can build a robust program that not only meets ethical objectives but also delivers tangible business benefits, making it a cornerstone of effective vendor management strategies.
7. Digital Vendor Management Platforms
Manually managing vendors with spreadsheets and email chains is unsustainable for scaling organizations. One of the most impactful vendor management strategies is adopting technology specifically built for the task. Digital Vendor Management Platforms are integrated software solutions that centralize, automate, and streamline the entire vendor lifecycle, from onboarding and risk assessment to performance monitoring and offboarding.
These platforms provide a single source of truth for all vendor-related data, giving stakeholders real-time visibility and control. Instead of fragmented information silos, you get a unified dashboard to manage contracts, track performance KPIs, assess compliance, and communicate effectively. For instance, enterprises use solutions like SAP Ariba or Oracle's supplier lifecycle management platform to manage complex global supply chains with data-driven precision.
How to Implement a Digital Vendor Management Platform
Successfully deploying a vendor management system (VMS) requires a strategic approach that goes beyond just purchasing software. The goal is to integrate the technology seamlessly into your existing workflows and business processes.
-
Define Clear Requirements: Before evaluating platforms, map out your current vendor management processes. Identify pain points, must-have features (e.g., automated onboarding, risk scoring), and key success metrics. This ensures you choose a solution that solves your specific problems.
-
Plan for Change Management: A new platform changes how people work. Develop a comprehensive plan for user training, communicate the benefits clearly, and secure buy-in from all stakeholders. Start with a core set of features and expand functionality gradually as users become more comfortable.
-
Prioritize Integration: Ensure the platform can integrate with your existing enterprise systems, such as your ERP and accounting software. To further streamline financial processes and enhance efficiency within your digital vendor management platforms, consider exploring advanced solutions like supplier payment automation. This creates a connected ecosystem, eliminates manual data entry, and ensures data consistency across your organization.
-
Maintain Data Governance: The platform is only as good as the data it holds. Establish clear data governance processes and provide ongoing user training to maintain high-quality, accurate vendor information. Regularly review platform utilization and optimize configurations to maximize its value. This approach is a core component of effective business process automation.
8. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis
Focusing solely on a vendor's upfront price is a common but costly mistake. A truly effective vendor management strategy looks beyond the initial sticker price to understand the full financial impact of a partnership. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis is a comprehensive financial methodology that calculates all direct and indirect costs associated with a vendor relationship over its entire lifecycle.
This approach provides a more accurate picture of a vendor's true cost, encompassing everything from implementation and training to maintenance, support, and eventual decommissioning. For instance, a data annotation platform with a lower subscription fee might require extensive internal engineering resources for integration and quality control, making its TCO significantly higher than a more expensive but fully managed solution. Adopting TCO analysis is crucial for making sound, long-term financial decisions.
How to Implement TCO Analysis
Implementing TCO requires a detailed and collaborative effort to identify and quantify costs that are often overlooked. The goal is to build a financial model that reflects the complete lifecycle of the vendor engagement.
-
Map the Entire Lifecycle: Identify every cost touchpoint from selection to exit. This includes:
- Acquisition Costs: Initial purchase price, procurement process, legal fees, and contract negotiation.
- Implementation & Integration Costs: Setup fees, data migration, software customization, and internal staff time.
- Operational & Maintenance Costs: Subscription fees, support contracts, user training, and necessary hardware or infrastructure upgrades.
- Risk & Exit Costs: Potential costs from vendor failure, data security breaches, and contract termination or transition to a new provider.
-
Involve All Stakeholders: Collaborate with IT, finance, legal, and the end-user departments to gather comprehensive cost data. The team that will use the vendor's service will have unique insights into hidden operational costs like training time and workflow adjustments. Ford Motor Company, for example, uses extensive TCO modeling for its manufacturing equipment, involving engineering, finance, and plant operations to capture every potential cost.
9. Agile Vendor Onboarding
Traditional vendor onboarding can be a slow, bureaucratic process that delays projects and frustrates new partners. Agile Vendor Onboarding flips the script by applying principles of speed, flexibility, and iterative improvement to the process. This strategy uses technology and streamlined workflows to qualify and enable vendors faster, reducing time-to-value while maintaining essential due diligence.
The core idea is to move away from a rigid, one-size-fits-all onboarding system. Instead, you create a dynamic, efficient experience that gets vendors ready to deliver value as quickly as possible. Consider Amazon's seamless seller onboarding that allows for near-immediate marketplace participation, or Uber's mobile-first system that rapidly activates new driver-partners. These models prioritize speed and user experience without sacrificing necessary compliance checks.
How to Implement Agile Vendor Onboarding
Implementing this strategy involves re-engineering your current processes to eliminate bottlenecks and leverage automation. It requires a mindset shift from gatekeeping to enablement.
-
Map and Automate: Document every step of your current onboarding journey to identify delays and repetitive tasks. Implement workflow automation tools to handle steps like initial data collection, document submission, and standard compliance checks.
-
Create Tiered Onboarding Tracks: Not every vendor requires the same level of scrutiny. Develop different onboarding paths based on vendor risk, complexity, and strategic importance. A low-risk provider of automated speech recognition (ASR) services might follow a fast-tracked, automated process, while a high-risk data processor undergoes a more intensive review. This targeted approach is one of the most effective vendor management strategies for balancing speed with security. You can learn more about finding specialized ASR partners and how to evaluate their capabilities in this guide to top ASR staffing companies.
-
Prioritize Communication: Use a central portal or platform to give vendors real-time visibility into their onboarding status. Automated notifications and clear checklists prevent confusion and reduce manual follow-up for both teams.
-
Gather Feedback and Iterate: Treat your onboarding process like a product. Regularly collect feedback from newly onboarded vendors to identify pain points and areas for improvement. Use this data to continuously refine and optimize the experience, ensuring it remains efficient and effective as your business scales.
Vendor Management Strategies Comparison Matrix
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Vendor Segmentation | Medium – multi-tier classification; regular updates needed | Moderate – assessment tools and analysis | Optimized resource allocation; focused management | Enterprises with varied vendor portfolios needing prioritization | Tailored management; risk prioritization; efficiency |
| Vendor Performance Scorecards and KPIs | High – data collection, metric design, and reporting | High – data systems and analysis personnel | Objective performance insights; continuous improvement | Organizations requiring detailed vendor performance tracking | Data-driven decisions; early issue ID; benchmarking |
| Risk-Based Vendor Assessment | High – comprehensive risk profiling and continuous monitoring | High – expert risk teams and monitoring tools | Proactive risk mitigation; improved resilience | Firms exposed to regulatory/compliance risks or high-impact vendors | Reduced disruptions; compliance; informed decisions |
| Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM) | High – system implementation and process standardization | High – CLM software, training, ongoing maintenance | Faster contract cycles; increased compliance | Organizations managing many contracts seeking automation | Visibility; streamlined workflows; reduced legal risk |
| Vendor Relationship Management (VRM) | High – requires ongoing collaboration and governance | High – time, skilled relationship managers | Strong partnerships; innovation; cost optimization | Businesses seeking strategic partnerships and innovation | Access to innovation; enhanced alignment; competitive advantage |
| Vendor Diversity and Inclusion Programs | Medium – program development and tracking metrics | Moderate – reporting systems and supplier development | Inclusive supply chain; enhanced brand reputation | Companies committed to social responsibility and regulatory compliance | Innovation from diversity; improved reputation; compliance support |
| Digital Vendor Management Platforms | High – technology deployment and integration | High – software investment, training, and maintenance | Centralized visibility; automation; faster onboarding | Enterprises aiming for digital transformation of vendor processes | Efficiency; data quality; advanced analytics |
| Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis | High – detailed cost modeling and financial expertise required | Moderate to High – financial analysts and data | Comprehensive vendor cost understanding; better ROI | Organizations needing full cost transparency for vendor selection | Accurate cost insight; improved financial planning; negotiation leverage |
| Agile Vendor Onboarding | Medium to High – automation setup and process redesign | Moderate – technology and process optimization | Reduced onboarding time; better vendor experience | Companies seeking fast, efficient vendor qualification | Speed; resource efficiency; compliance through automation |
Building Your Future-Proof Vendor Ecosystem
The journey from viewing vendors as mere suppliers to embracing them as strategic partners is the definitive shift that separates market leaders from the rest. The nine vendor management strategies detailed in this article are not isolated tactics but interconnected components of a holistic, future-proof framework. Mastering this framework is no longer a “nice-to-have” operational efficiency; it is a core competitive necessity in a world driven by specialization, agility, and third-party data.
Moving beyond transactional relationships allows your organization to build a resilient, innovative, and high-performing vendor ecosystem. This strategic evolution transforms your supply chain from a potential point of failure into a powerful engine for growth, enabling you to scale teams rapidly, access specialized expertise on demand, and leverage high-quality data to fuel your most ambitious projects, from AI model training to global market expansion.
Key Takeaways: From Theory to Action
Recapping the critical pillars we've explored, the path to vendor management excellence is paved with intentional, data-driven actions. The most impactful takeaways for immediate implementation include:
- Strategic Segmentation is Foundational: Not all vendors are created equal. By implementing Strategic Vendor Segmentation, you can focus your most intensive relationship management efforts on partners who have the greatest impact on your business outcomes, while applying more standardized, efficient processes for transactional suppliers.
- Data-Driven Decisions are Non-Negotiable: Gut feelings and anecdotal evidence are no longer sufficient. The implementation of Vendor Performance Scorecards and a rigorous Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis replaces subjectivity with objective, quantifiable metrics, ensuring every decision is backed by solid data.
- Proactive Management Outperforms Reactive Fixes: Waiting for problems to arise is a costly mistake. A proactive approach, integrating Risk-Based Vendor Assessment, robust Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM), and a focus on Vendor Relationship Management (VRM), allows you to anticipate challenges, mitigate threats, and collaboratively solve problems before they escalate.
Your Next Steps: Building a Robust Vendor Management Program
Transforming your vendor management approach can seem daunting, but progress starts with targeted, incremental steps. Use the strategies outlined as a diagnostic tool to assess your current capabilities and identify your most significant opportunities for improvement.
- Conduct a Vendor Audit: Begin by mapping your current vendor landscape. Use the principles of Strategic Vendor Segmentation to categorize your existing partners. Who are your critical, strategic partners, and who are your tactical or transactional suppliers? This initial audit will reveal where your greatest risks and opportunities lie.
- Pilot a Scorecard Program: Select one or two of your strategic vendors and collaboratively develop a Vendor Performance Scorecard. Define a handful of meaningful KPIs that align with your business goals. This pilot program will help you refine your process before a full-scale rollout.
- Review Your Onboarding Process: Evaluate your current vendor onboarding experience. Is it agile, clear, and efficient? Implementing an Agile Vendor Onboarding process is often a quick win that can immediately improve new partner relationships and accelerate their time-to-value.
By focusing on these practical first steps, you begin building the muscle memory for a more sophisticated and effective vendor management strategy. The goal is to create a dynamic ecosystem where your partners are actively contributing to your innovation, efficiency, and long-term success. This is how you stop simply managing vendors and start leading a network of partners dedicated to mutual growth.
Ready to elevate your vendor management from an operational task to a strategic advantage? Zilo AI provides end-to-end manpower and high-quality data services, acting as a strategic partner to help you implement these advanced strategies effectively. Let us help you build a resilient, scalable, and high-performing vendor ecosystem. Learn more about how Zilo AI can support your growth.

