In today's competitive business environment, success isn't just about having resources; it's about deploying them with precision and foresight. From harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and managing vast data pipelines to securing the right talent for critical roles, every decision can dictate the trajectory of a project and the company itself. Ineffective resource management directly leads to budget overruns, stalled projects, and critical missed opportunities.
The key to unlocking sustainable growth and maintaining a competitive edge lies in adopting sophisticated resource allocation strategies. This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a comprehensive roundup of ten proven methods specifically tailored for modern, data-driven businesses. Whether you are a tech startup aiming for rapid scaling or an established enterprise seeking to optimize operations, these strategies offer a clear roadmap for success.
We will explore how to balance risk, align resources with core strategic goals, and leverage dynamic tools to stay ahead of market demands. This article is designed to be a practical toolkit, providing actionable insights you can implement immediately. By mastering these approaches, you can transform your resource management from a complex challenge into a powerful driver of competitive advantage. This ensures every dollar, hour, and data point is invested for maximum impact. For instance, leveraging specialized partners for data annotation or managed staffing can be a crucial component in executing these strategies effectively, allowing your core team to focus on high-value activities. You will learn how to make smarter, more strategic decisions that propel your business forward.
1. Priority-Based Allocation
Priority-Based Allocation is a foundational resource allocation strategy where resources-including capital, personnel, and technology-are funneled to projects and initiatives based on their strategic importance. Instead of distributing resources evenly, this method ensures that the most critical objectives receive the necessary support to succeed before any lower-priority items are addressed. It forces organizations to make conscious, deliberate choices about what truly drives value.
This approach is about saying "no" to good ideas to say "yes" to the best ones. It’s a disciplined framework that aligns daily actions with long-term strategic goals, preventing resource dilution across too many initiatives. By concentrating firepower on high-impact areas, businesses can accelerate progress where it matters most, a tactic essential for any company leveraging data-driven insights and AI.
How to Implement Priority-Based Allocation
Implementing this strategy requires a structured, data-informed process. Vague priorities lead to ineffective allocation, so clarity is paramount. A classic example is Apple's strategic decision to focus intensely on a few core products like the iPhone and MacBook, allocating the vast majority of its R&D and marketing resources to them, rather than diversifying too broadly.
Follow these steps for effective implementation:
- Establish Clear Criteria: Define what "priority" means for your business. Use a scoring model based on metrics like potential ROI, alignment with strategic goals, market opportunity, and risk level.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Bring together leaders from different departments to debate and agree on priorities. This creates buy-in and ensures a holistic view of the business's needs.
- Rank and Allocate: Score all potential projects or initiatives against your defined criteria. Rank them from highest to lowest and allocate resources starting from the top of the list until they are exhausted.
- Regularly Review: Priorities are not static. Market conditions, competitive pressures, and internal capabilities change. Schedule quarterly or bi-annual reviews to reassess and adjust your priority list.
Key Insight: The power of Priority-Based Allocation lies not just in funding the top items but in explicitly defunding or postponing the bottom ones. This disciplined approach is one of the most effective resource allocation strategies for achieving focused growth.
2. Portfolio-Based Resource Allocation
Portfolio-Based Resource Allocation treats an organization's initiatives as a diversified portfolio of investments. Rather than evaluating projects in isolation, this comprehensive approach manages them collectively, balancing risk, return, and strategic alignment across the entire business. It shifts the mindset from picking individual "winners" to building a resilient, high-performing collection of ventures.
This strategy, popularized by frameworks like the Boston Consulting Group's Growth-Share Matrix, allows businesses to optimize overall performance. It ensures resources are distributed not just to sure bets but also to calculated risks and long-term innovation. For companies leveraging AI and data services, this means balancing core operational improvements with speculative, high-growth R&D projects.
The infographic below summarizes a sample portfolio's key metrics, demonstrating how this strategy provides a high-level view of resource distribution and expected outcomes.
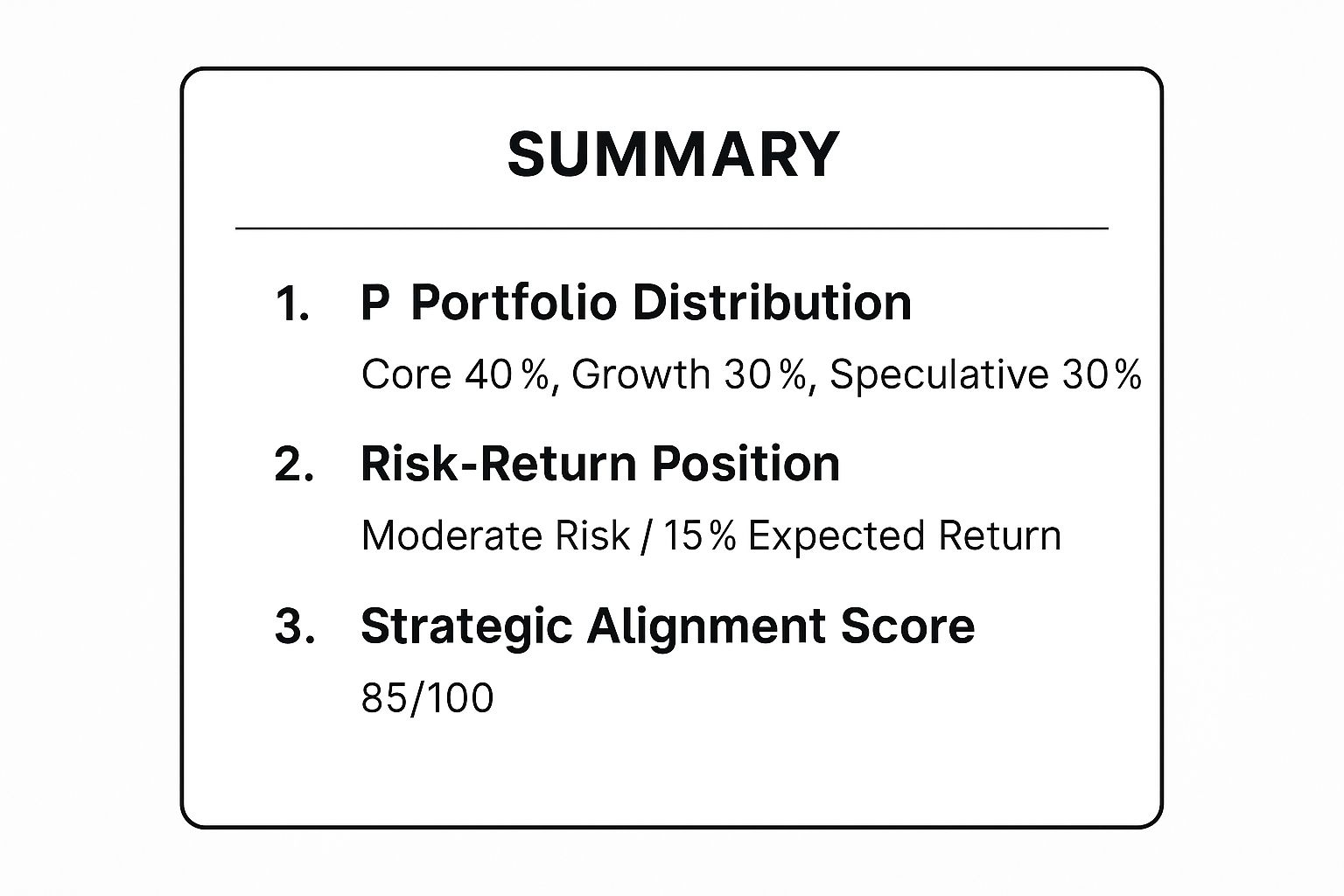
This balanced distribution ensures that while core business is maintained, the company is also investing in future growth and breakthrough innovations, all while maintaining a strong strategic focus.
How to Implement Portfolio-Based Resource Allocation
Effective implementation requires a sophisticated, holistic view of all business activities. A classic example is Google (Alphabet), which manages a diverse portfolio ranging from its core search business (cash cow) to speculative "Other Bets" like Waymo. This allows them to fund innovation with profits from established products.
Follow these steps for effective implementation:
- Categorize Initiatives: Classify all projects into strategic buckets. A common model is McKinsey's Three Horizons: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging opportunities), and Horizon 3 (speculative bets).
- Establish Risk Tolerance: Define your organization's appetite for risk. This will guide how you balance your portfolio between safe, incremental projects and high-risk, high-reward ventures.
- Analyze and Balance the Portfolio: Use portfolio management tools to map projects based on metrics like potential ROI, cost, and risk. Adjust allocations to achieve the desired balance, ensuring you aren't over-invested in one area. If you're looking to enhance this process, adopting a culture of data-driven decision-making is crucial.
- Conduct Regular Reviews: The portfolio is a living entity. Hold regular review sessions (quarterly is common) to re-evaluate projects, kill underperformers, and reallocate resources to capitalize on new opportunities.
Key Insight: The main advantage of Portfolio-Based Resource Allocation is its ability to manage risk at a macro level. By intentionally diversifying investments across different risk profiles and timelines, an organization can pursue ambitious innovation without jeopardizing its core stability.
3. Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB)
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) is a radical and highly effective resource allocation strategy that challenges the status quo. Instead of adjusting the previous period’s budget, ZBB requires every department to justify every expense from a "zero base" for each new budget cycle. This method forces a rigorous evaluation of all activities and expenditures, ensuring they align directly with current strategic objectives and add tangible value.
This approach dismantles ingrained spending habits and eliminates budgetary bloat by forcing managers to ask "Why do we need this?" rather than "How much did we spend last year?" It shifts the focus from incremental increases to intentional, value-driven spending. For organizations implementing costly AI initiatives or scaling data services, ZBB ensures that every dollar invested is scrutinized for its contribution to core business goals.
How to Implement Zero-Based Budgeting
Effective ZBB implementation demands a cultural shift towards accountability and a deep, granular understanding of operational needs. A prime example is 3G Capital, which famously used ZBB to drive immense operational efficiency at companies like Kraft Heinz and Anheuser-Busch InBev by questioning every line item.
Follow these steps for effective implementation:
- Identify Decision Packages: Break down all business activities into "decision packages" that can be individually evaluated and ranked. Each package should detail its purpose, cost, benefits, and consequences if not funded.
- Evaluate and Rank: Analyze each decision package based on its necessity and contribution to strategic goals, not its historical funding level. Rank these packages in order of importance, creating a clear hierarchy for resource allocation.
- Allocate from Zero: Fund the highest-ranked packages first, moving down the list until the budget is fully allocated. This process inherently prioritizes critical functions and value-creating initiatives.
- Utilize Technology: Implement financial planning and analysis (FP&A) software to streamline the data collection, evaluation, and reporting process. Technology is crucial for managing the complexity of a full ZBB rollout.
Key Insight: Zero-Based Budgeting is more than a cost-cutting tool; it's a strategic framework that instills a culture of cost-consciousness and operational excellence. It links every dollar of spending directly to value creation, making it one of the most powerful resource allocation strategies for lean, ambitious organizations.
4. Agile Resource Allocation
Agile Resource Allocation is a dynamic and flexible approach where resources are distributed in short, iterative cycles. Instead of locking down budgets and teams for long-term projects, this strategy emphasizes rapid adaptation, continuous feedback, and incremental progress. Resources are allocated to small, cross-functional teams for fixed periods, known as sprints, allowing for regular reassessment and reallocation based on evolving priorities and real-time performance data.
This method swaps rigid annual planning for responsive, short-term deployment, making it one of the most effective resource allocation strategies for volatile markets. It empowers teams to pivot quickly without bureaucratic delays, ensuring that personnel and capital are always directed toward the most valuable activities at any given moment. This iterative flow is crucial for businesses leveraging AI and data, where project requirements can change rapidly based on new insights.

How to Implement Agile Resource Allocation
Implementing an agile approach requires a cultural shift toward empowerment, transparency, and continuous learning. It moves decision-making closer to the teams doing the work. A prime example is Spotify's famous "squad" model, where small, autonomous teams are given the resources and authority to tackle specific missions, allowing the company to innovate at scale.
Follow these steps for effective implementation:
- Form Small, Cross-Functional Teams: Create dedicated teams (often called squads or pods) with all the skills needed to deliver a specific outcome, such as developers, data scientists, and marketers.
- Allocate in Short Cycles: Assign resources for short, time-boxed periods, typically two-to-four-week sprints. At the end of each cycle, review progress and re-evaluate priorities for the next one.
- Establish Clear Communication Channels: Use tools like daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and shared backlogs to maintain transparency and alignment. This is where business process automation can greatly enhance efficiency. Learn more about optimizing these workflows on ziloservices.com.
- Maintain Strategic Alignment: While teams operate autonomously, their efforts must align with overarching business goals. Leadership's role is to set the strategic direction and clear success metrics, not to micromanage tasks.
Key Insight: Agile Resource Allocation thrives on the principle of "just-in-time" decision-making. Instead of predicting the future, it builds the capacity to react to it, making it ideal for fast-paced environments where innovation and speed are paramount.
5. Activity-Based Resource Allocation
Activity-Based Resource Allocation is a granular method that connects resources directly to the specific tasks and activities that consume them. Instead of allocating budgets to broad departments or projects, this strategy drills down to understand which activities drive costs and create value. It provides unparalleled visibility into how resources are truly being used, shifting the focus from "what we spend" to "what we spend it on."
This approach, popularized by scholars like Robert Kaplan and Robin Cooper, is a powerful tool for process optimization and efficiency. It reveals inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement that are often hidden within traditional budget structures. By linking costs to the activities that generate them, businesses can make more informed decisions about process re-engineering, automation, and outsourcing, making it one of the most precise resource allocation strategies available.
How to Implement Activity-Based Resource Allocation
Effective implementation requires a detailed mapping of business processes to understand the flow of work and resource consumption. This method shines in environments where operational efficiency is a key competitive advantage. A classic example is the Toyota Production System, which meticulously allocates resources to activities that add value for the customer while ruthlessly eliminating waste (muda) from non-value-added activities.
Follow these steps for effective implementation:
- Map Key Business Activities: Begin by identifying and documenting all the core activities performed within a process or department. This could range from "processing a customer order" to "annotating a dataset."
- Identify Primary Cost Drivers: For each activity, determine the primary driver of its cost. For data annotation, the driver might be the number of images processed or the hours spent by annotators.
- Allocate Resources to Activities: Assign costs from your general ledger (like salaries, software licenses, and overhead) to the specific activities they support. This creates a clear link between spending and operational output.
- Analyze and Optimize: With a clear cost-per-activity, you can identify high-cost or low-value tasks. Use this data to prioritize automation, streamline workflows, or reallocate resources from inefficient activities to more impactful ones.
Key Insight: Activity-Based Resource Allocation transforms budgeting from a top-down financial exercise into a bottom-up operational analysis. It empowers teams to see the direct financial impact of their daily activities, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and cost-consciousness.
6. Dynamic Resource Allocation
Dynamic Resource Allocation is a highly adaptive strategy where the distribution of resources is adjusted in real-time based on live performance data, shifting priorities, and fluctuating market conditions. Instead of setting allocations on a quarterly or annual basis, this method leverages algorithms and continuous data feedback to optimize resource deployment automatically. It is one of the most powerful resource allocation strategies for businesses operating in volatile environments.
This approach transforms resource management from a static, periodic planning exercise into a continuous, automated process. It ensures that capital, personnel, and computational power are always directed where they can generate the most value at any given moment. For data-centric organizations, this means maximizing efficiency and responsiveness by letting intelligent systems make rapid allocation decisions.
How to Implement Dynamic Resource Allocation
Successful implementation hinges on robust data infrastructure and a commitment to algorithmic decision-making. A prime example is Amazon Web Services (AWS) Auto Scaling, which automatically adjusts computing resources for applications based on real-time traffic, ensuring performance without over-provisioning. Similarly, Uber's surge pricing and driver allocation algorithm dynamically balances supply and demand.
Follow these steps to get started:
- Invest in Analytics Capabilities: A strong foundation in data collection, processing, and real-time analytics is non-negotiable. Your systems must be able to ingest and interpret performance data instantly.
- Start with Simple Algorithms: You don't need a complex AI from day one. Begin with rule-based systems (e.g., "if metric X exceeds Y, allocate Z more resources") and gradually increase sophistication as you gather more data. For businesses looking to fast-track this process, exploring low-code and no-code AI platforms can be a strategic accelerator.
- Ensure High-Quality Data: The adage "garbage in, garbage out" is especially true here. Your allocation algorithms are only as good as the data they are fed. Implement rigorous data governance and validation processes.
- Maintain Human Oversight: While the goal is automation, human supervision is crucial, especially in the early stages. Set thresholds and alerts to have experts review and override automated decisions when necessary.
Key Insight: Dynamic Resource Allocation thrives on data and speed. It is best suited for environments with high variability, such as digital advertising, e-commerce traffic management, or cloud computing, where manual adjustments are too slow to be effective.
7. Balanced Scorecard Resource allocation
Balanced Scorecard Resource Allocation is a strategic management system that shifts the focus from purely financial metrics to a more holistic view. Popularized by Robert Kaplan and David Norton, this approach allocates resources across four critical business perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Business Processes, and Learning & Growth. It ensures that short-term financial gains do not come at the expense of long-term capabilities like customer satisfaction or employee development.
This strategy prevents the common pitfall of over-investing in one area while neglecting others essential for sustainable success. By tying resource allocation directly to a comprehensive set of strategic objectives, it ensures that capital, talent, and technology are deployed in a balanced way. For data-driven organizations, this means funding not just immediate AI model deployment but also the underlying data infrastructure and team training needed for future innovation.
How to Implement Balanced Scorecard Resource Allocation
Effective implementation requires translating a high-level strategy into a connected map of measurable objectives. This framework links resource requests directly to strategic outcomes across all four perspectives. A classic example is Mobil Oil (now ExxonMobil), which used this method to transform its strategy, aligning its budget with new goals for customer intimacy and operational excellence, leading to a dramatic performance turnaround.
Follow these steps for effective implementation:
- Define Your Strategy Map: For each of the four perspectives, define clear strategic objectives. For example, a financial goal might be "Increase Revenue," while a learning goal could be "Develop AI Expertise."
- Select Key Metrics: Assign specific, measurable KPIs to each objective. Limit the number of metrics per perspective to avoid over-complication and maintain focus on what truly matters.
- Align and Allocate Resources: Fund initiatives that directly support your chosen metrics and objectives. If an initiative doesn't clearly advance a goal on your scorecard, its resource allocation should be questioned.
- Ensure Leadership Commitment: The balanced scorecard must be driven from the top down. Leadership must consistently use it to guide decisions, review performance, and adjust resource allocation strategies.
Key Insight: The Balanced Scorecard’s strength is its ability to create a cause-and-effect narrative that connects every dollar spent to a strategic outcome. It forces a disciplined conversation about trade-offs, ensuring that investments in long-term growth are not sacrificed for short-term financial targets.
8. Constraint-Based Resource Allocation
Constraint-Based Resource Allocation is a powerful method derived from the Theory of Constraints, which posits that every complex system has at least one factor limiting its performance. Instead of spreading resources thin, this strategy concentrates them on identifying and alleviating the single biggest bottleneck. The goal is to optimize the performance of the entire system, not just individual parts.
This approach prevents wasteful spending on areas that are already performing adequately while the real bottleneck remains unaddressed. By focusing resources with surgical precision on the weakest link, organizations can unlock disproportionate gains in overall throughput and efficiency. This is one of the most effective resource allocation strategies for complex systems like supply chains, software development pipelines, or service delivery models.
How to Implement Constraint-Based Resource Allocation
Effective implementation requires a systems-thinking mindset and a relentless focus on the flow of value. A classic example is a software development team where new features are developed quickly but get stuck for weeks in the quality assurance (QA) phase. Instead of hiring more developers, this strategy would allocate resources, like automated testing tools or additional QA personnel, directly to the testing bottleneck.
Follow these steps for effective implementation:
- Identify the True Constraint: Analyze your entire workflow or process to find the single step that limits the output of the entire system. This could be a person, a team, a piece of equipment, or even a policy.
- Exploit the Constraint: Before adding resources, ensure the bottleneck is operating at its maximum possible capacity. Optimize its schedule, processes, and performance without significant investment.
- Subordinate Everything Else: Align all other processes and resources to support the constraint. Non-bottleneck parts of the system should operate at the pace of the bottleneck, preventing overproduction and wasted effort.
- Elevate the Constraint: If the constraint still limits system performance after exploitation and subordination, allocate capital, technology, or personnel to increase its capacity. This is the point where you invest.
- Repeat the Process: Once a constraint is resolved, a new one will emerge elsewhere in the system. The process of identification and optimization is continuous.
Key Insight: Constraint-Based Resource Allocation flips traditional thinking on its head. Instead of asking "Where can we improve?", it asks "What one thing is stopping us from improving everywhere?". Answering this question directs resources to the point of maximum leverage.
9. Resource Allocation Using Options Theory
Resource Allocation Using Options Theory treats strategic investments not as one-time, all-or-nothing commitments, but as financial options. This advanced method values flexibility, allowing organizations to make small initial investments to gain the right, but not the obligation, to make larger follow-on investments later. It's a powerful way to manage uncertainty and capitalize on future opportunities as they become clearer.
This approach is especially suited for high-risk, high-reward environments like technology development or pharmaceutical R&D, where initial outcomes are unknown. Instead of betting the farm on an unproven concept, you buy an "option" on its future success. This framework makes it one of the most sophisticated resource allocation strategies for navigating volatile markets and pioneering innovation.
How to Implement Resource Allocation Using Options Theory
Successfully applying this theory requires shifting from a static NPV (Net Present Value) mindset to a dynamic one that quantifies the value of managerial flexibility. For instance, a tech company might fund a small pilot project for a new AI feature. If the pilot shows promise (the "option" is in the money), they can exercise the option by allocating significant resources for a full-scale launch.
Follow these steps for effective implementation:
- Identify Key Uncertainties: Pinpoint the major variables that will determine a project's success or failure, such as market adoption, technological feasibility, or competitor response. These uncertainties are what make the "option" valuable.
- Structure Investments as Options: Break down large projects into phased investments. The initial funding phase is the cost of the option, and subsequent funding stages are the "exercise price." A prime example is how venture capital firms fund startups in rounds (Seed, Series A, B, C), only committing more capital after specific milestones are met.
- Set Clear Decision Points: Establish explicit triggers or milestones that will prompt a decision to continue, expand, delay, or abandon the initiative. These decision points are when you evaluate whether to exercise your option.
- Value Flexibility Explicitly: Use financial models like the Black-Scholes model or binomial trees to assign a tangible monetary value to the flexibility you've created. This helps justify smaller, strategic bets that traditional ROI analysis might overlook.
Key Insight: The core principle of Options Theory is that in an uncertain world, the ability to adapt is a valuable asset. This strategy allows you to limit downside risk on unproven ideas while retaining massive upside potential, a critical capability for any business investing in breakthrough AI or data-driven ventures.
10. Participatory Resource Allocation
Participatory Resource Allocation is a collaborative strategy where stakeholders at various levels are actively involved in making decisions about how resources are distributed. Rather than a top-down mandate, this democratic method taps into the collective intelligence of the group, incorporating diverse perspectives from those closest to the work, including employees, community members, or department teams. It fosters a sense of ownership and transparency.
This approach is built on the principle that better decisions are made when a wider range of insights is considered. It boosts morale and buy-in, as participants feel heard and valued. For tech companies and data science teams, this can mean involving engineers and data analysts in budgeting for new tools or allocating time for R&D projects, ensuring the choices made are practical and well-supported on the ground.
How to Implement Participatory Resource Allocation
Effective implementation requires structure to prevent chaos and ensure decisions align with broader strategic objectives. The goal is inclusive, informed decision-making, not just an open forum. A well-known example is the city of Porto Alegre, Brazil, which pioneered participatory budgeting, allowing citizens to directly decide how a portion of the municipal budget is spent.
Follow these steps for effective implementation:
- Establish Clear Guidelines: Define the scope of participation. Clarify which decisions are open for input, who is eligible to participate, and what the final decision-making process looks like.
- Provide Necessary Information: Empower participants with the data they need to make informed choices. This includes transparent access to budget constraints, strategic goals, and performance data of past initiatives.
- Use a Structured Process: Employ frameworks like workshops, surveys, or voting platforms to gather and weigh input systematically. This ensures every voice can contribute in a fair and organized manner.
- Balance Participation with Authority: While input is democratic, the final decision may still rest with leadership. Communicate how the collective input will be used to guide the final allocation, maintaining a balance between inclusivity and accountability.
Key Insight: Participatory Resource Allocation transforms resource planning from a purely financial exercise into a powerful tool for employee engagement and cultural development. This is one of the resource allocation strategies that directly builds trust and aligns the entire organization around shared goals.
Top 10 Resource Allocation Strategies Comparison
| Method | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Priority-Based Allocation | Low – clear ranking and simple process | Moderate – requires priority data | Ensures critical projects get resources | Emergency response, military, healthcare triage | Ensures critical focus, transparency |
| Portfolio-Based Allocation | High – requires sophisticated analysis | High – advanced tools and continuous review | Balanced risk-return, strategic alignment | Large corporations, VC funds, diversified portfolios | Risk reduction, strategic balance |
| Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) | High – starts from zero baseline, detailed review | High – time and administrative heavy | Eliminates waste, cost-consciousness | Cost control focused orgs, government | Waste elimination, critical evaluation |
| Agile Resource Allocation | Moderate-High – iterative, requires culture change | Moderate – agile training and teams | Rapid adaptation, faster delivery | Tech firms, innovation environments | High adaptability, faster time-to-market |
| Activity-Based Allocation | High – requires detailed activity mapping | High – substantial administrative overhead | Improved cost management, process focus | Manufacturing, services, process improvements | Accurate resource planning, process optimization |
| Dynamic Resource Allocation | Very High – needs advanced tech and algorithms | Very High – real-time data and automation | Optimal utilization, quick response | Tech platforms, dynamic markets | Real-time optimization, reduced bias |
| Balanced Scorecard Allocation | High – strategic alignment, multiple metrics | Moderate – ongoing measurement | Balanced growth, long-term success | Strategic management in diverse organizations | Comprehensive view, balanced investment |
| Constraint-Based Allocation | Moderate-High – systems thinking required | Moderate – monitoring bottlenecks | Maximizes system performance | Manufacturing, supply chain, software bottlenecks | Focus on constraints, system-wide improvement |
| Options Theory Allocation | Very High – complex financial modeling | High – specialized analysis | Flexibility, staged investment decisions | R&D, venture funding, strategic acquisitions | Values flexibility, reduces risk |
| Participatory Allocation | Moderate – requires facilitation and structure | Moderate – stakeholder coordination | Increased buy-in, transparency | Community projects, democratic budgeting | Stakeholder engagement, improved transparency |
From Strategy to Execution: Your Next Steps in Resource Mastery
Navigating the landscape of resource allocation can feel like charting a course through unpredictable waters. However, as we have explored, a well-defined map and a reliable compass can make all the difference. The ten distinct resource allocation strategies detailed in this article, from the foundational logic of Priority-Based Allocation to the sophisticated, forward-looking approach of Options Theory, are not merely theoretical models. They are practical frameworks designed to bring order, clarity, and strategic intent to your operational core.
The journey from understanding these strategies to mastering them begins with a candid self-assessment. The models we've covered, including Agile Resource Allocation and Zero-Based Budgeting, share a common prerequisite: organizational clarity. You cannot effectively allocate resources if you don't have a crystal-clear view of your strategic objectives, project pipelines, and current resource deployment. The true power lies not in choosing a single, rigid strategy but in thoughtfully blending them to create a hybrid approach that mirrors your unique organizational DNA.
Synthesizing the Strategies for Maximum Impact
Your organization's ideal approach might combine the fiscal discipline of Zero-Based Budgeting for annual planning, the flexibility of Agile Resource Allocation for your development sprints, and the holistic view of a Balanced Scorecard to ensure long-term alignment. The key is to move beyond a "one-size-fits-all" mentality and embrace a tailored, adaptive system.
For instance, a fast-growing tech startup might lean heavily on Dynamic and Constraint-Based Allocation to manage the chaotic, high-stakes environment of scaling. In contrast, a large enterprise in the healthcare sector could use Activity-Based Allocation to optimize costs in established departments while applying Portfolio-Based Allocation to manage its pipeline of innovative R&D projects. The common thread is a commitment to data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement.
Your Actionable Roadmap to Resource Mastery
Moving from theory to practice requires deliberate, sequential steps. Here is a practical roadmap to begin implementing more effective resource allocation strategies today:
- Conduct a Resource Audit: Before you can chart a new course, you need to know your current position. Map out where every resource, from personnel and budget to technology and data, is currently allocated. Identify areas of underutilization, bottlenecks, and misalignment with strategic goals.
- Define and Rank Your Priorities: Use a framework like the Balanced Scorecard or simple priority-based ranking to establish a clear hierarchy of what matters most. This step is non-negotiable; without it, every resource request will seem equally urgent.
- Pilot a New Model: Choose one high-impact, low-risk project or department to pilot a new allocation strategy. Whether it's implementing Zero-Based Budgeting for a single team or adopting Agile principles for a specific project, a small-scale pilot allows you to learn, adapt, and build buy-in without disrupting the entire organization.
- Invest in the Right Tools: Modern resource allocation is powered by data. Implement or upgrade project management software, financial planning tools, and analytics platforms that provide real-time visibility into resource utilization and project progress.
- Foster a Culture of Transparency: Effective allocation requires open communication. Ensure that team leaders and members understand why decisions are made. When people see the connection between resource allocation and strategic success, they are more likely to support the process.
Mastering resource allocation is not a final destination but a continuous journey of refinement. It’s about transforming a routine administrative task into a powerful engine for growth, innovation, and competitive advantage. By embracing these principles and taking deliberate action, you can ensure that your most valuable resources are always focused on your most critical opportunities, turning strategic vision into tangible reality.
Ready to supercharge your resource allocation for data-intensive projects? Zilo AI provides on-demand access to skilled human intelligence for data annotation, transcription, and translation, allowing you to scale your AI and ML initiatives without the burden of fixed overhead. Execute your strategy with precision by visiting Zilo AI to learn how our flexible workforce solutions can become your ultimate competitive advantage.

