At its core, video annotation is the process of adding descriptive labels to video footage, frame by frame, to teach a computer what it’s seeing. This crucial step turns a simple video into a powerful training tool for artificial intelligence and computer vision systems.
What Are Video Annotation Services?
Imagine you’re trying to teach an AI model to spot a running dog in a park. You can't just feed it thousands of hours of park footage and hope for the best. You need to go through the video and explicitly point out, "This is the dog," and "This is the action of running," in every single frame where it appears.
That’s exactly what video annotation services do. They provide the human touch and precision needed to label, tag, and track objects and movements within video. This process essentially creates a detailed study guide for an AI, translating a visual stream of pixels into structured data that a machine learning algorithm can actually learn from.
From Raw Pixels to Actionable Insights
The ultimate goal here is to create what we call "ground-truth data." Think of it as the official answer key for the AI's final exam. When the AI model tries to identify something on its own, its prediction is checked against this perfectly labeled data to see how well it did. The closer it gets, the smarter it becomes.
This foundational work is what makes so many incredible applications possible today:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Teaching self-driving cars to distinguish between a pedestrian, a cyclist, and a traffic cone is only possible with meticulously annotated video.
- Retail Analytics: Ever wonder how a cashier-less store works? It uses AI trained on video to track products being taken off shelves and analyze customer movement patterns.
- Healthcare Innovations: In medicine, AI models can be trained on annotated surgical videos to help identify instruments, or even spot subtle anomalies in an MRI that a human eye might miss.
- Security and Surveillance: Modern security systems rely on this technology to do everything from detecting an intruder to monitoring crowd flow in a busy airport.
At its heart, video annotation is the bridge between human perception and machine understanding. It translates the dynamic, unstructured nature of video into the structured, logical format that algorithms require to function effectively.
Why Human Expertise Is Crucial
You might think a computer could just do this on its own, but the truth is, video is packed with nuance that still requires a human brain. People are needed to interpret context, deal with objects that are partially hidden (occlusion), and ensure every label is perfectly consistent from one frame to the next.
This is where a dedicated service provider comes in. They don’t just supply the annotators; they bring the specialized software, project management experience, and multi-layered quality control processes needed to handle these massive, complex projects.
Ultimately, video annotation is far more than just drawing boxes on a screen. It's about meticulously building the datasets that allow machines to see and interpret the world a little more like we do. The quality of that annotation directly dictates how well the final AI model will perform.
Exploring the Core Types of Video Annotation

When it comes to video labeling, one size definitely does not fit all. The right technique hinges entirely on what you want your AI model to learn. Think of it like this: you wouldn't use a sledgehammer for delicate woodwork, and you wouldn't use a tiny chisel to break up concrete. Similarly, video annotation services use different methods to get the right level of detail.
Let's walk through the most common techniques, starting with the basics and moving toward the more complex, granular methods. Each one gives your AI a different kind of lesson.
Bounding Boxes: The Foundational Rectangle
The simplest and most common starting point is bounding box annotation. It’s exactly what it sounds like: drawing a four-sided box around every object you care about in a video—a car, a person, a traffic light. This tells the AI, "An object of this type is right here, within these coordinates."
This method is quick, efficient, and perfect for object detection tasks where the general location is more important than the exact shape. The downside? Its simplicity. A bounding box always captures some background pixels along with the object, which can introduce a bit of noise into the training data. For most applications, that’s perfectly fine. But if you need to teach an AI the precise silhouette of an irregular object, like a puddle or a specific plant, a simple box just won't cut it.
Polygon and Segmentation: For Precision and Detail
When you need more precision, you have to move beyond the box. Polygon annotation is a big step up in detail. Instead of a rigid rectangle, annotators click a series of points around an object's perimeter to trace its exact shape. This is fantastic for things that don't fit neatly into a box, like a person stretching their arms out or a uniquely shaped chair.
For the absolute highest level of accuracy, there's semantic segmentation. Imagine coloring in every single pixel that belongs to an object, like a digital coloring book. An AI trained on this data doesn't just see a car; it understands the car's exact boundary, pixel by pixel. This level of detail is crucial for medical imaging AI that needs to find the precise edge of a tumor or for autonomous vehicles that must distinguish perfectly between the road and the sidewalk. As you can imagine, this method is powerful but also the most time-intensive and expensive.
The demand for these advanced techniques is a major reason why video and image annotation make up a huge slice of the data labeling market, accounting for 41% to 46% of all annotation work. The sheer complexity of video data requires skilled teams to handle tasks like segmentation and tracking. You can dive deeper into these market trends in AI annotation to see the full picture.
Keypoints and Tracking: For Understanding Motion
So far, we've talked about identifying objects. But what about understanding movement? That’s where keypoint annotation, sometimes called pose estimation, comes in. This involves marking critical points on an object to map its form. On a person, you might label the elbows, knees, and wrists to teach an AI about human posture and action. This is the go-to method for sports analytics, helping to analyze an athlete's technique, or for robotics, where a machine learns to mimic human movements.
Finally, object tracking is what brings it all together across time. This technique assigns a unique ID to an object in the first frame and then follows it through the entire video clip. It ensures the AI knows that the blue car in frame one is the exact same blue car in frame 500, even if it disappears behind a truck for a few seconds. This is the magic that separates video annotation from static image labeling—it gives the model a sense of context and continuity, allowing it to understand behavior, predict where an object will go, and make sense of complex events.
To help you decide which approach is right for your project, here’s a quick comparison of the techniques we've covered.
Comparison of Video Annotation Techniques
This table compares common video annotation types, their best use cases, and complexity levels to help you choose the right method for your project.
| Annotation Type | Description | Best Used For | Complexity Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bounding Boxes | Drawing a rectangular box around an object. | General object detection where precise shape isn't critical (e.g., counting cars on a highway). | Low |
| Polygon Annotation | Tracing the exact outline of an object with a series of connected points. | Labeling irregularly shaped objects that don't fit well in a box (e.g., a pedestrian with outstretched arms). | Medium |
| Semantic Segmentation | Assigning a class label to every pixel in the video frame. | High-precision tasks requiring pixel-perfect accuracy (e.g., medical imaging, autonomous driving). | High |
| Keypoint Annotation | Marking specific points of interest on an object (e.g., joints on a person). | Pose estimation, gesture recognition, and analyzing movement (e.g., sports analytics, robotics). | Medium-High |
| Object Tracking | Assigning a unique ID to an object and following it across multiple frames. | Analyzing behavior over time, trajectory prediction, and action recognition (e.g., retail foot traffic analysis). | High |
Choosing the right annotation method is a balancing act between the detail your model needs and the time and budget you have. If you want to explore the differences between these labeling techniques in more detail, check out our guide on image annotation services.
Video Annotation in the Real World
All the theory behind bounding boxes and semantic segmentation really comes to life when you see it applied to actual, real-world problems. High-quality video annotation services aren't just for research papers; they're the fuel for AI systems actively changing how entire industries get work done. From making our roads safer to helping doctors improve patient care, accurately labeled video is the unseen engine driving real innovation.
This whole process is about turning raw, meaningless footage into intelligent data. It’s how we teach machines to see, understand, and react to the world just like we do. Let’s take a look at how this is making a real difference in a few key areas.
Making Autonomous Vehicles a Reality
The road to fully autonomous driving is paved with, quite literally, petabytes of meticulously annotated video. For a self-driving car to navigate a busy city street, it has to identify everything in its path—instantly and without error.
This is where video annotation becomes a matter of life and death. Human annotators have to painstakingly label frame after frame of training data to teach the car's AI the crucial difference between things like:
- A pedestrian and a lamppost. They might both be tall, vertical shapes, but one of them can suddenly step into the road.
- A plastic bag and a small animal. One is a harmless piece of litter, while the other requires the car to slow down and react cautiously.
- A shadow and a pothole. Mistaking a shadow is no big deal, but failing to see a pothole could be dangerous.
Object tracking is especially important here. It allows the AI to predict where a cyclist or another car is heading, which is essential for making safe, proactive decisions. Without this deep layer of human-guided learning, the dream of self-driving cars would stay stuck in the garage.
Reshaping How We Shop
In the cutthroat world of retail, knowing your customer is everything. Video annotation is now powering a new wave of smart retail solutions that are fine-tuning everything from store layouts to the checkout experience.
By analyzing annotated video from in-store cameras, retailers can train AI to handle some pretty complex tasks. Think about frictionless checkout systems, like those you see in an Amazon Go store. They rely on AI that can track exactly which items you pick up and put in your bag. This requires incredibly precise object tracking and segmentation to tell the difference between hundreds of similar-looking products on crowded shelves.
Annotated video also gives retailers a bird's-eye view of foot traffic, showing them which parts of the store are "hot zones" and how long customers linger at certain displays. This kind of insight is gold for optimizing product placement and making the whole shopping trip better.
This tech also helps keep shelves stocked by automatically spotting when they’re empty or when items are in the wrong place. Retailers are turning what used to be simple security footage into a rich source of business intelligence, creating stores that are more efficient and much more pleasant to shop in.
Advancing Healthcare and Medical Science
The impact of video annotation in healthcare is nothing short of profound. It’s giving medical professionals new tools for diagnosis, surgical training, and patient monitoring. AI models trained on carefully labeled medical videos can work alongside doctors, helping them achieve better outcomes for their patients.
Take the operating room, for example. Surgeons can now be guided by AI systems that have learned from thousands of hours of annotated surgical procedures. These models can identify anatomical structures, recognize specific surgical tools, and even flag potential issues in real time. Keypoint annotation, for instance, can track a surgeon’s hand movements to assess their technique and offer feedback.
It doesn’t stop at surgery. The technology is being used to analyze videos from endoscopies and ultrasounds to spot anomalies like polyps or tumors that the human eye might miss. In physical therapy, AI can watch a patient's exercises, making sure they’re doing them correctly to ensure a faster, safer recovery.
Innovating in Agriculture and Beyond
The uses for video annotation go far beyond just cars and stores. In modern agriculture, or "AgriTech," drones fly over huge fields, capturing video. Once that footage is annotated, AI models can learn to:
- Spot crop diseases by picking up on subtle changes in the color or texture of leaves.
- Monitor the health of livestock by analyzing how the animals are behaving and moving.
- Optimize irrigation systems by seeing which parts of a field are too dry or too wet.
From sports analytics, where keypoint annotation breaks down an athlete’s form, to security systems that can recognize unusual behavior, the pattern is the same. Video annotation services provide the critical human insight needed to build AI systems that solve tangible, practical problems in almost every industry you can think of.
The Blueprint for a Successful Annotation Workflow
A high-quality dataset is never an accident. It’s born from a structured, methodical process that turns raw video into AI-ready training data. Professional video annotation services rely on a proven workflow, breaking down massive projects into clear, manageable stages to ensure the final output is both accurate and reliable.
Think of it like building a house. You wouldn't start hammering nails without a detailed architectural plan, a solid foundation, and multiple quality checks along the way. In the same way, a successful annotation project needs careful planning from start to finish. Skipping steps can lead to costly mistakes that end up misleading your AI model.
This structured workflow is the backbone of the entire AI annotation market, a sector projected to balloon from USD 1.96 billion in 2025 to a staggering USD 17.37 billion by 2034. This explosive growth underscores the rising demand for systematic and scalable data labeling. You can read more about the growth of the AI annotation market and what's driving it.
The Five Stages of Video Annotation
Every project, no matter how simple or complex, moves through a series of essential steps. This assembly-line approach guarantees consistency, accuracy, and efficiency at every turn.
Project Scoping and Guideline Creation: This is the foundation of everything. Project managers sit down with you to define the exact rules of the game. What objects need labeling? How should tricky edge cases be handled? The result is a set of crystal-clear guidelines, packed with visual examples, that gets every single annotator on the same page.
Data Preparation and Platform Setup: Next, all your raw video footage is collected, organized, and uploaded to a specialized annotation platform. The data might be pre-processed to clean it up, and the tools are configured specifically for the project's needs. There are many different computer vision annotation tools out there, and choosing the right one is key.
The Annotation Phase: With clear instructions in hand, the trained annotators get to work. They meticulously label objects, track movements, and identify events frame by frame, applying the project rules with precision. This is where the raw data truly begins its transformation.
Rigorous Quality Assurance (QA): The first pass of labels is never the final product. A multi-layered QA process kicks in, where senior annotators or a completely separate team reviews the work. They're looking for accuracy, consistency across frames, and strict adherence to the guidelines. Techniques like consensus scoring—where several annotators label the same clip—are often used to iron out ambiguities and boost reliability.
Data Delivery and Feedback Loop: Once the dataset passes all quality checks, it’s delivered in the format you need. But the job isn't quite done. A good partner establishes a feedback loop, using insights from the project to refine the guidelines and improve the workflow for the next batch of data.
A well-defined workflow isn't just a to-do list; it's a system built to guarantee data integrity. Each step acts as a filter, catching potential errors and ensuring the final dataset gives the AI model a true and accurate picture of reality to learn from.
The flowchart below shows how this process is adapted for different industries, from automotive to retail.
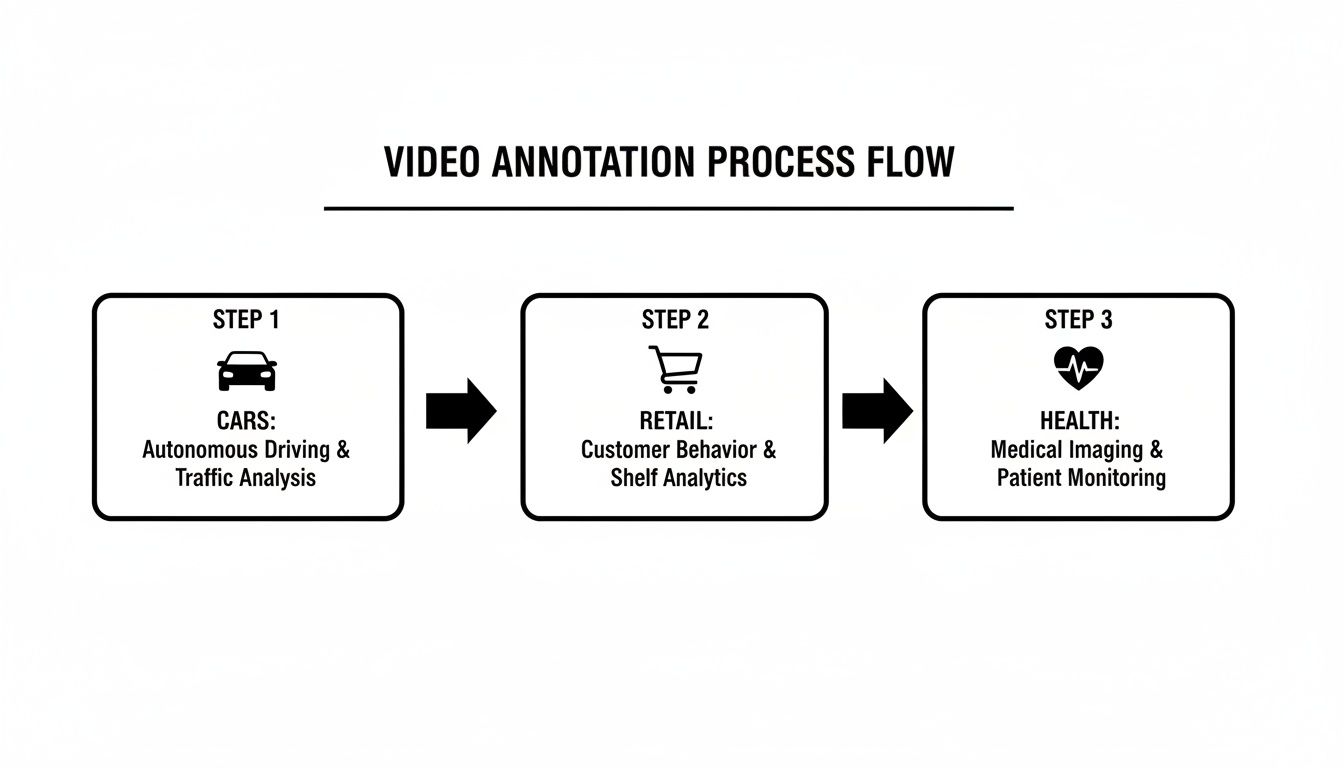
As you can see, while the specific applications change, the core workflow provides a consistent and reliable structure for success. By following this systematic approach, you make sure your investment in data annotation pays off with a powerful, effective training dataset for your computer vision models.
How to Choose the Right Video Annotation Partner
Picking a partner for your video annotation services is a decision that will make or break your AI project. It’s every bit as important as designing the model itself. Why? Because the quality of your training data directly fuels your model's performance, and the right partner is the guardian of that quality.
Think of it less like outsourcing a task and more like hiring a specialized extension of your own team. A great partner doesn’t just blindly label data; they dig in to understand your goals, foresee potential roadblocks, and deliver datasets that are clean, consistent, and reliable. Choosing poorly can set you back with noisy data, blown deadlines, and a model that completely fails in the real world.
The market for these services is growing fast. What was a USD 0.18 billion industry in 2026 is on track to more than double to USD 0.41 billion by 2035, growing at a compound annual rate of 9%. This growth is largely driven by companies outsourcing AI training tasks, with the Asia-Pacific region commanding about 40% of the market share. You can learn more about the trends shaping the video annotation market to get a better sense of where things are headed.
Quality and Accuracy Protocols
First things first: you absolutely have to scrutinize a vendor’s commitment to quality. Simply asking if they produce "high-quality" data won't cut it. You need to get into the weeds of their actual process. High accuracy isn’t an accident; it’s the direct result of a systematic, multi-layered approach.
Start by asking them to walk you through their Quality Assurance (QA) workflow. A solid partner will have a process with multiple checkpoints, not just a single review at the end. Look for established methods like:
- Peer Review: One annotator’s work is systematically checked by another.
- Consensus Scoring: Multiple annotators label the same data, and a senior reviewer resolves any disagreements.
- Gold Sets: Using pre-labeled data as a benchmark to regularly test annotator performance and catch any inconsistencies.
Don't be shy about asking for their internal accuracy metrics. A transparent vendor should be able to share data on their typical error rates and prove how they measure and maintain their standards.
Scalability and Flexibility
Your data needs today probably won't be your data needs tomorrow. A partner who can handle your initial pilot project is good, but you need one who can scale with you from a few hundred videos to tens of thousands. Scalability is more than just having a large workforce; it's about the project management and technical infrastructure needed to handle massive volume without letting quality slip.
Ask them how they ramp up (or down) as a project’s needs change. How quickly can they onboard and train new annotators to hit a tight deadline? How do their systems handle a sudden flood of new data? A flexible partner will adapt to your rhythm, keeping your project on track no matter what.
A partner's true value is revealed when a project's scope changes. Their ability to adapt, scale, and maintain quality under pressure is the ultimate test of their capability and a sign of a healthy, long-term relationship.
Security and Confidentiality Measures
For many companies—especially in healthcare, finance, or autonomous tech—data is extremely sensitive. Handing this data over to a third party requires total confidence in their security protocols. This is a non-negotiable.
Make sure the vendor has serious data protection measures in place, covering both physical and digital security. Ask about their compliance with international standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2. Dig into their data handling procedures, from secure transfer protocols to strict access control policies. A trustworthy partner will be completely open about their security framework and ready to sign iron-clad non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) to protect your work.
Tools, Technology, and Domain Expertise
Finally, take a close look at the tools they use and their actual understanding of your industry. The right technology can make a world of difference in efficiency and accuracy. Are they using modern annotation platforms with AI-assisted features like object tracking and interpolation to speed things up? Or are they stuck using clunky, manual tools?
Just as important is their domain expertise. A partner who genuinely understands the nuances of your field—whether it's medical imaging, retail analytics, or agricultural tech—will create far better annotation guidelines and produce more relevant data. They'll grasp the context behind your requests, which means fewer mistakes and a much more valuable dataset in the end. For more pointers, take a look at our in-depth article on choosing from top data annotation service providers.
Answering Your Top Video Annotation Questions
When you're gearing up for a new video annotation project, a few practical questions always come to the surface. How much will this cost? How do I know the quality will be good enough? Should we use humans or automation?
Getting solid answers to these questions is crucial. It helps you set a realistic budget, manage expectations with your team, and pick the right partner for the job. Let's break down the most common questions we hear from people just like you.
How Much Do Video Annotation Services Cost?
There’s no simple, one-size-fits-all price tag for video annotation. The cost really depends on two big things: the pricing model your vendor uses and how complex your project is.
Think of it like hiring a contractor to renovate your kitchen. The final bill depends on whether they charge by the hour or by the project, and whether you’re just replacing countertops or gutting the whole room. It’s the same with annotation.
Most providers use one of three main pricing structures:
- Per-Hour Model: This is the most popular approach. You pay an hourly rate for the annotator's time, which can range anywhere from $5 to $50 an hour based on their location and expertise. It's a great fit for projects where the complexity might change or the scope isn't perfectly defined from the start.
- Per-Frame or Per-Video Model: With this model, you pay a set price for each frame or video clip that gets labeled. This works best for massive, repetitive projects where the task is predictable—like drawing simple bounding boxes on thousands of very similar frames.
- Per-Object Model: If your focus is on labeling specific items within a video, you might pay for each object annotated. This is a smart choice when the number of objects changes dramatically from one frame to the next, because you only pay for the exact work being done.
Naturally, the more detailed the work, the higher the cost. Drawing simple boxes is always going to be cheaper than painstakingly outlining an object down to the last pixel with semantic segmentation.
How Do You Ensure the Quality of Annotations?
This is, without a doubt, the most important question you can ask. High-quality data is everything. If your dataset is full of mistakes, your AI model will just learn bad habits, and its real-world performance will suffer.
Any annotation service worth its salt has a multi-layered Quality Assurance (QA) process baked into its workflow. This isn't just a quick check at the end; it's a systematic approach to catching and fixing errors at every step.
Here are a few of the most effective quality control methods you should look for:
- Peer Review: A second, often more senior, annotator reviews the work of the first. This simple two-person system is incredibly effective at catching human error and making sure everyone is following the project rules.
- Consensus Scoring: When a task is tricky or subjective, the same piece of data is sent to several annotators. The final label is decided by a majority vote, or a senior reviewer steps in to break the tie. This is a powerful technique for boosting accuracy on nuanced tasks.
- Gold Sets: A "gold set" is a small batch of data that’s been perfectly labeled by an in-house expert. Annotators are tested against this perfect set from time to time. If their scores dip, it’s a clear sign they need a refresher on the guidelines.
The entire point of a robust QA process is to create a reliable "ground truth." This is a dataset so accurate it can act as the final answer key for training and testing your AI model. For any serious computer vision project, this is non-negotiable.
Manual Versus Automated Annotation
People often ask if it's better to have humans or machines do the labeling. The real answer is: you need both. It's not about choosing one over the other, but about striking the right balance between human precision and machine efficiency.
Manual annotation is the classic approach where a person meticulously labels every frame by hand. It delivers the best possible accuracy, especially for complex scenes that would confuse an algorithm. The downside? It can be slow and costly, particularly for huge volumes of data.
Automated annotation flips the script by using an AI model to do the first pass of labeling. This is incredibly fast, but the quality is only as good as the pre-existing model. It often stumbles when it sees new or unusual objects and simply lacks a human's common-sense understanding of the world.
That's why the Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) approach has become the industry standard. It truly gives you the best of both worlds. An AI model does the initial heavy lifting, and then human annotators jump in to review, correct, and fine-tune the labels. This hybrid system speeds everything up dramatically without sacrificing the high-quality results that only human oversight can guarantee.
Ready to build the high-quality datasets your AI models need to succeed? Zilo AI provides expert video annotation services with a focus on accuracy, scalability, and security. Our skilled teams and proven workflows ensure your computer vision projects are built on a foundation of reliable data. Contact us today to discuss your project.

